How to manage your DNS records (A, AAAA, CNAME, MX, SRV, TXT) through DNS Zone Manager
Table of Contents
How to access your DNS zone editor
To add, edit or delete a DNS record, go to Site Tools > Domain > DNS Zone Editor. You can manage DNS records only if your domain is pointed to our name servers. If we believe that the domain you wish to manage is not properly pointed, you will see a warning with information about the proper name servers that you should use.

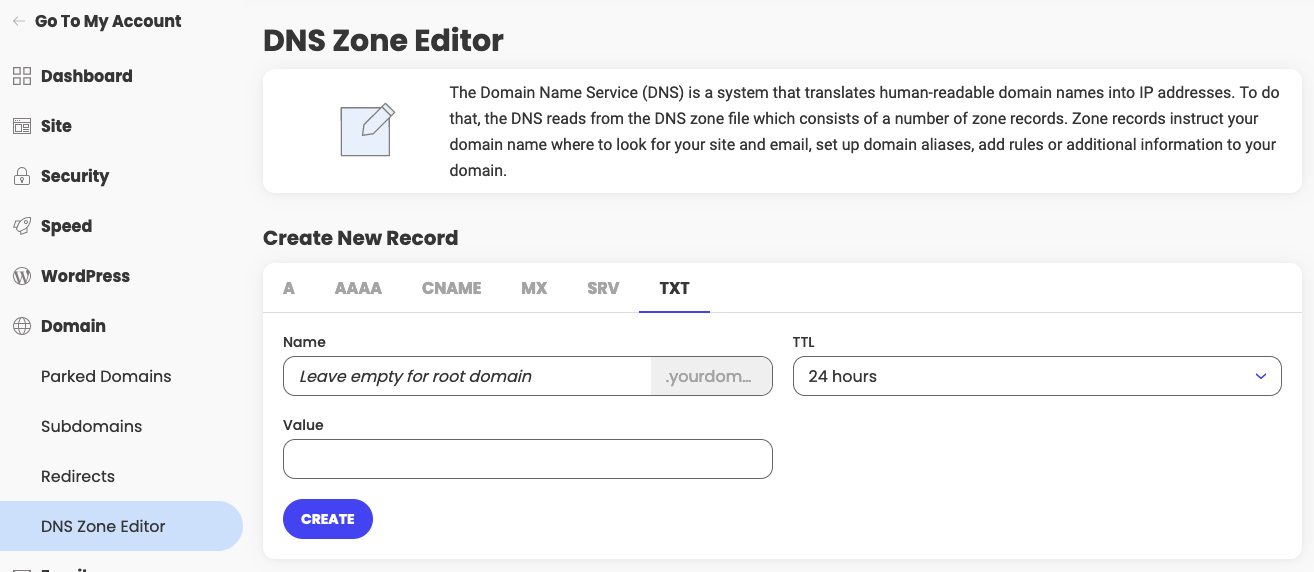
How to Create new DNS record
Once you access Site Tools > Domain > DNS Zone Editor, in the Create New Record section you can click the tab corresponding to the type of record you wish to create. It can be an A, AAAA, CNAME, MX, SRV or TXT record. Then fill in the required information and click Create.
How to edit or delete existing DNS record
Once you access Site Tools > Domain > DNS Zone Editor, in the Manage DNS Records section you can edit and delete existing DNS records. Next to the desired record, click the pencil icon if you want to edit it or the trashcan icon if you want to delete it. Apply the required changes in the pop-up that appears and click Confirm.
How to reset your DNS records
You can only reset individual records to their default values by editing them. Click the pencil icon next to the record you wish to reset, and then adjust the values to the previous default values. If you’re unsure of the default values, that were initially configured with your hosting account, you can contact our support team for assistance.
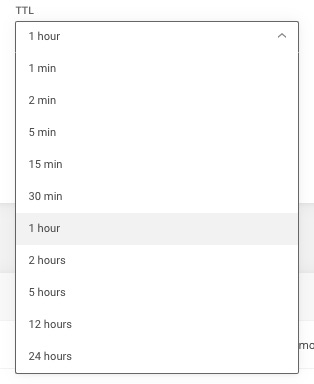
TTL (time to live) setting for DNS records
In the required information for all record types there is a drop-down menu, called TTL (time to live). It indicates the time DNS servers store the respective record in cache. For the automatically created default records we have set this value to what we believe is most efficient. When you create a new record, you may set it to whatever value you believe is ok. If you are not sure, 1 hour is a good choice.
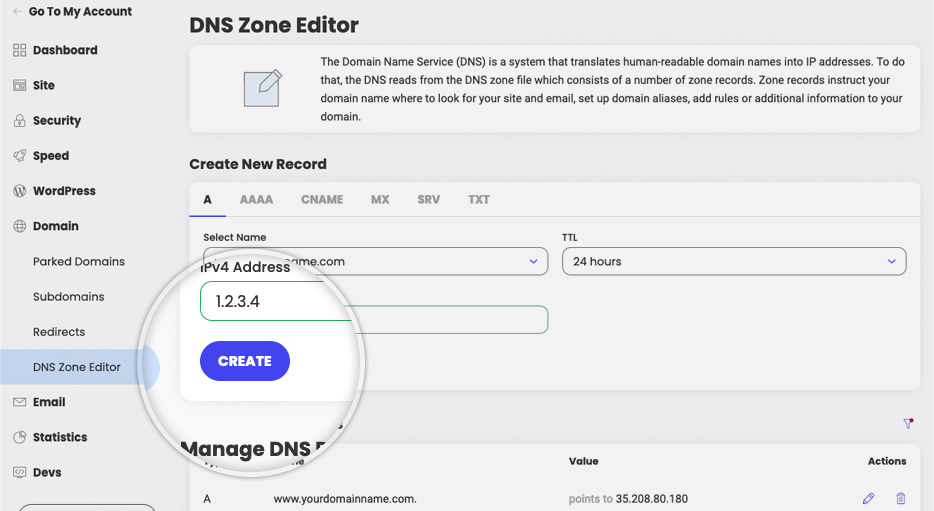
A record settings
The A record specifies the IP addresses from IPv4 (internet protocol version 4) corresponding to your domain and its subdomains. By default this is your site IP address with us. If you want to edit an A record so that part of your site points to another server, you need to know the IPv4 address of this server and insert it in the corresponding field.

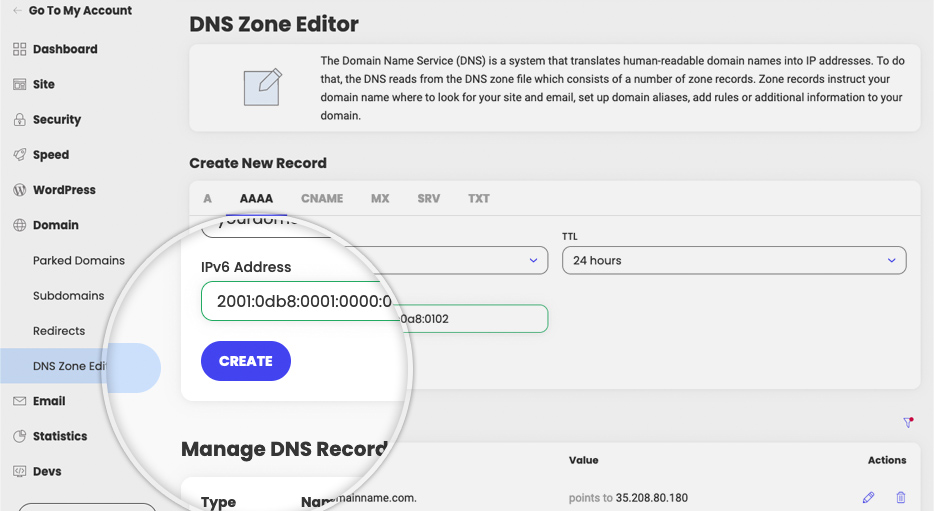
AAAA record settings
The AAAA record specifies the IP addresses from IPv6 (internet protocol version 6) corresponding to your domain and its subdomains. If you want to add or edit an AAAA record you need to add the IPv6 address you wish to be used.
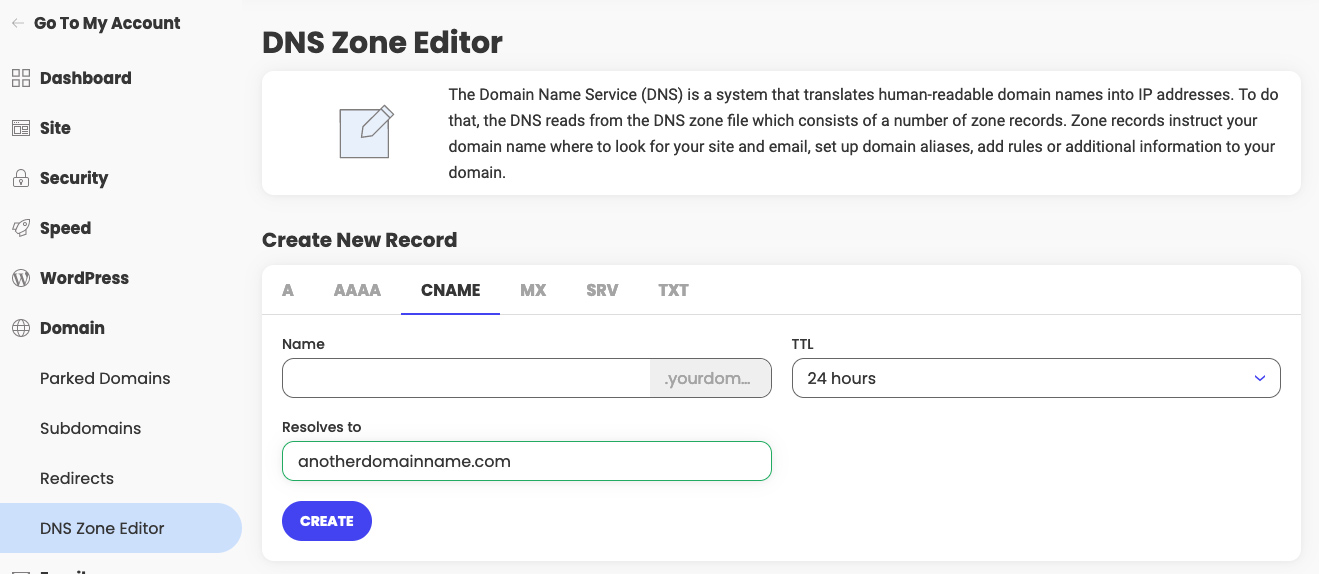
CNAME record settings
The CNAME record specifies redirects from your domain’s subdomains to other domains/subdomains. A valid domain/host should be provided as a destination for the CNAME record as it does not accept IP addresses.
MX record settings
The MX record specifies where the emails for your domain should be delivered. You may have multiple delivery options that can be prioritized with the help of the priority setting. This means that the initial delivery attempt will go to the destination with the lowest priority, and if not successful will try the next one. By default clients have 3 MX records set to our mail service.
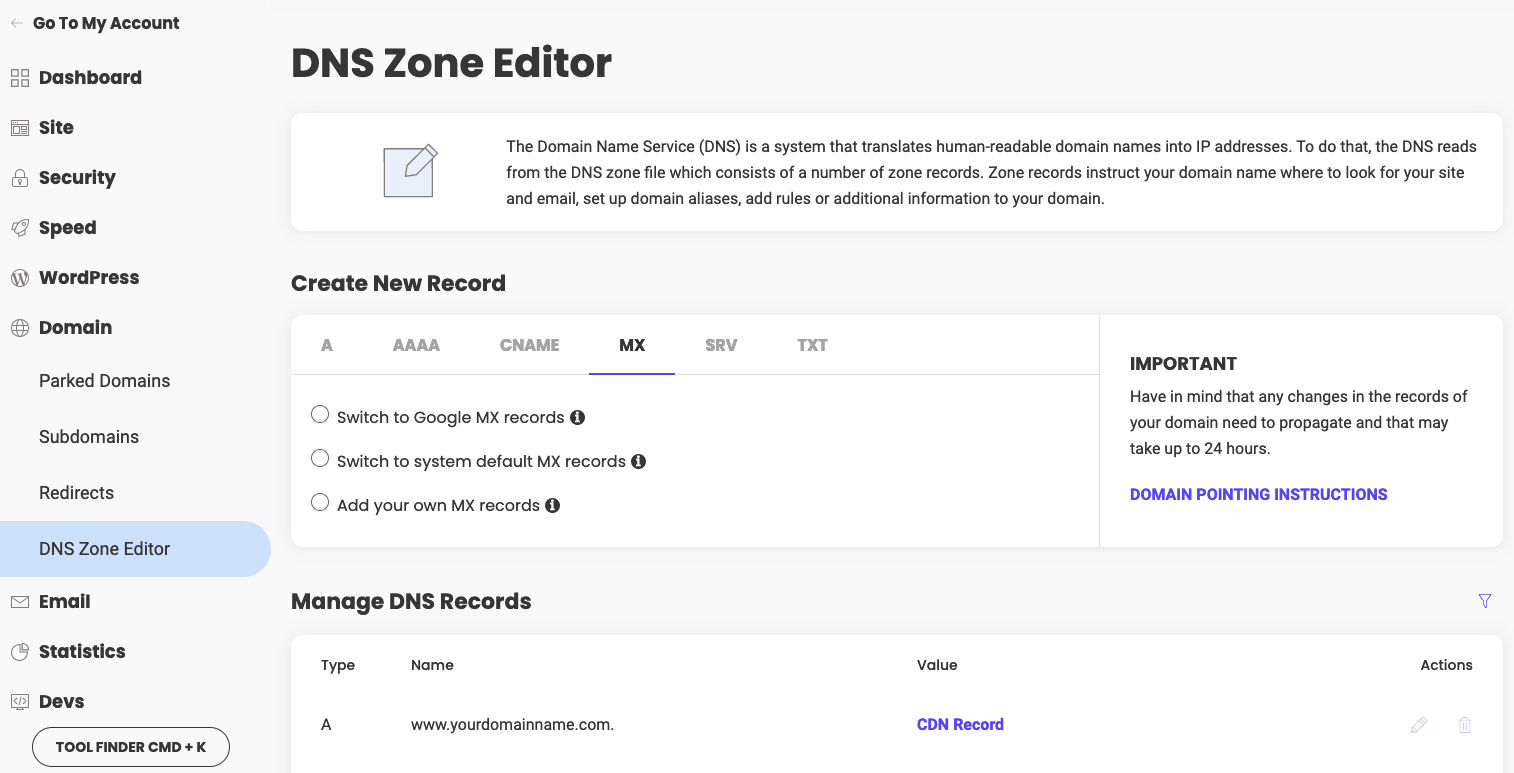
You can use the Switch to Google MX records button to automatically point your mail service to Google or the Add your own MX records button to manually add new MX records for your domain.
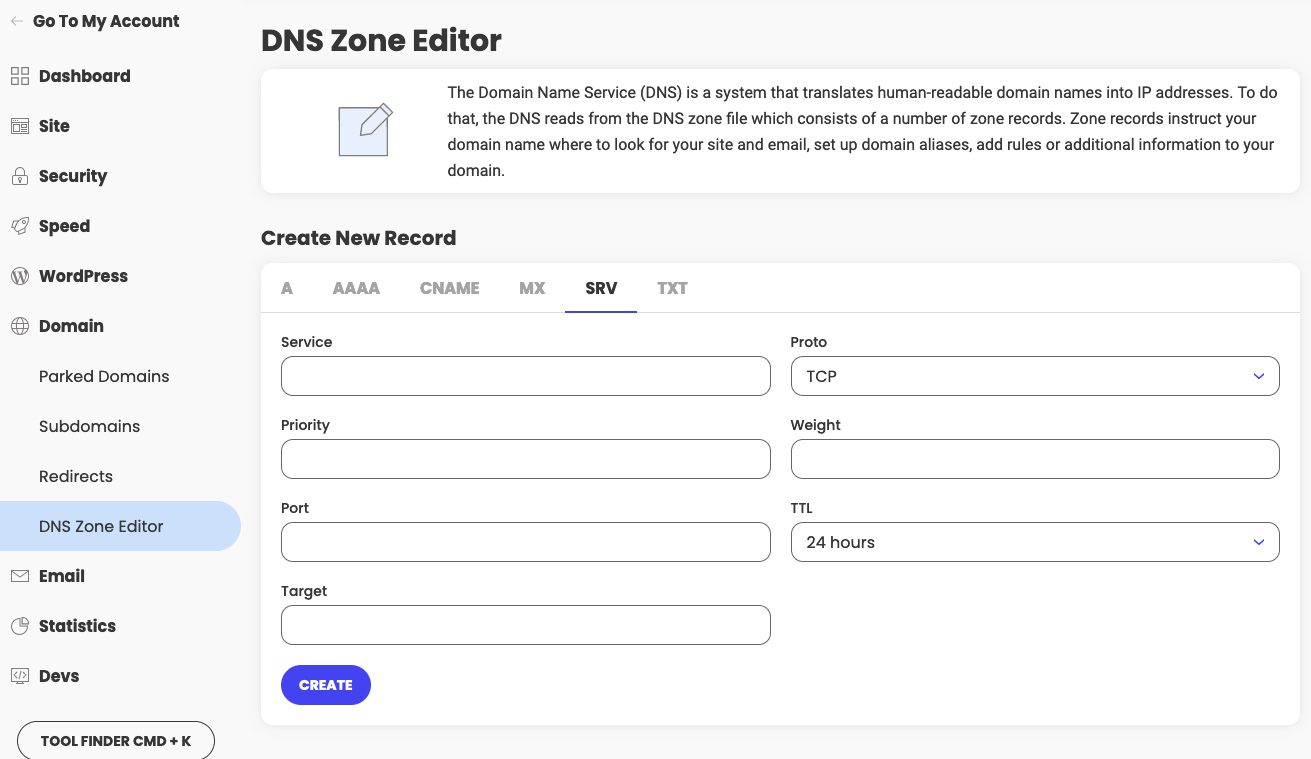
SRV record settings
A SRV record (Service Record) specifies the location, i.e., the hostname and port number, of servers for specified services. To set it up you need to provide the following values:
- Service – the name of the service, without underscore;
- Proto – the protocol of the service (usually TCP or UDP);
- TTL – time to live;
- Priority – lower values mean more preferred;
- Weight – used for records with the same priority (higher value means more preferred);
- Port – the number of the port;
- Target – the hostname of the machine where the service is running.
TXT record settings
The TXT records are used to store text-based information related to your domain. They may be needed for domain ownership verification and are also commonly used for storing SPF and DKIM data also needed for email spoofing prevention.